Key words: hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose; PVC with high polymerization degree; small experiment; polymerization; localization.
The application of China hydroxypropyl methylcellulose instead of imported one to the production of PVC with high polymerization degree was introduced. The effects of two kinds of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose on the properties of PVC with high polymerization degree were investigated. The results showed that it was feasible to substitute domestic hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose for imported one.
High-degree-of-polymerization PVC resins refer to PVC resins with an average degree of polymerization of more than 1,700 or a slightly cross-linked structure between molecules. Compared with ordinary PVC resin, high-polymerization PVC resin has high resilience, small compression set, good heat resistance, aging resistance, fatigue resistance and wear resistance. It is an ideal rubber substitute and can be used in automobile sealing strips, wire and cable, medical catheters, etc.
The production method of PVC with high degree of polymerization is mainly suspension polymerization. In the production of the suspension method, the dispersant is an important auxiliary agent, and its type and amount will directly affect the particle shape, particle size distribution, and plasticizer absorption of the finished PVC resin. The commonly used dispersion systems are polyvinyl alcohol systems and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and polyvinyl alcohol composite dispersion systems, and domestic manufacturers mostly use the latter .
1 Main raw materials and specifications
The main raw materials and specifications used in the test are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose selected in this paper is consistent with the imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, which provides a prerequisite for the substitution test in this paper.
2 Test content
2. 1 Preparation of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose solution
Take a certain amount of deionized water, put it into a container and heat it to 70°C, and gradually add hydroxypropyl methylcellulose under constant stirring. The cellulose floats on the water at first, and then is gradually dispersed until it is evenly mixed. Cool the solution to volume.
Table 1 Main raw materials and their specifications
|
Raw material name |
Specification |
|
Vinyl chloride monomer |
Quality score≥99. 98% |
|
Desalinated water |
Conductivity≤10. 0 μs/cm, pH value 5. 00 to 9. 00 |
|
Polyvinyl alcohol A |
Alcoholysis degree 78. 5% to 81. 5%, ash content≤0. 5%, volatile matter≤5. 0% |
|
Polyvinyl alcohol B |
Alcoholysis degree 71. 0% to 73. 5%, viscosity 4. 5 to 6. 5mPa s, volatile matter≤5. 0% |
|
Polyvinyl alcohol C |
Alcoholysis degree 54. 0% to 57. 0% , viscosity 800 ~ 1 400mPa s, solid content 39. 5% to 40. 5% |
|
Imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose A |
Viscosity 40 ~ 60 mPa s, methoxyl mass fraction 28% ~ 30%, hydroxypropyl mass fraction 7% ~ 12%, moisture≤5. 0% |
|
Domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose B |
Viscosity 40 ~ 60 mPa · s, methoxyl mass fraction 28% ~ 30%, hydroxypropyl mass fraction 7% ~ 12%, moisture ≤5. 0% |
|
Bis(2-ethyl peroxydicarbonate) hexyl ester) |
Mass fraction [( 45 ~ 50) ± 1]% |
2. 2 Test method
On the 10 L small test device, use imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to conduct benchmark tests to determine the basic formula of the small test; use domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to replace imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for testing; The PVC resin products produced by hydroxypropyl methylcellulose were compared, and the feasibility of replacing domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose was studied. According to the results of the small test, the production test is carried out.
2. 3 Test steps
Before the reaction, clean the polymerization kettle, close the bottom valve, add a certain amount of desalinated water, and then add the dispersant; close the kettle cover, vacuumize after passing the nitrogen pressure test, and then add vinyl chloride monomer; after cold stirring, add the initiator ; Use circulating water to raise the temperature in the kettle to the reaction temperature, and add ammonium bicarbonate solution in a timely manner during this process to adjust the pH value of the reaction system; when the reaction pressure drops to the pressure specified in the formula, add a terminator and a defoamer, and release the solution. The finished product of PVC resin was obtained by centrifugation and drying, and sampled for analysis.
2. 4 Analysis methods
According to the relevant test methods in enterprise standard , the viscosity number, apparent density, volatile matter (including water) and plasticizer absorption of 100 g PVC resin of finished PVC resin were tested and analyzed; The average particle size of the PVC resin was tested; the morphology of the PVC resin particles was observed using a scanning electron microscope.
3 Results and Discussion
3. 1 Comparative analysis of the quality of different batches of PVC resin in small-scale polymerization
Press 2. According to the test method described in 4, each batch of small-scale finished PVC resin was tested, and the results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 results of different batches of small test
|
Batch |
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
Apparent density/(g/mL) |
Average particle size/μm |
Viscosity/(mL/g) |
Plasticizer absorption of 100 g PVC resin/g |
Volatile matter/% |
|
1# |
Import |
0.36 |
180 |
196 |
42 |
0.16 |
|
2# |
Import |
0.36 |
175 |
196 |
42 |
0.20 |
|
3# |
Import |
0.36 |
182 |
195 |
43 |
0.20 |
|
4# |
Domestic |
0.37 |
165 |
194 |
41 |
0.08 |
|
5# |
Domestic |
0.38 |
164 |
194 |
41 |
0.24 |
|
6# |
Domestic |
0.36 |
167 |
194 |
43 |
0.22 |
It can be seen from Table 2: The apparent density, viscosity number and plasticizer absorption of the obtained PVC resin are relatively close by using different cellulose for small test; the resin product obtained by using the domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose formula The average particle size is slightly smaller.
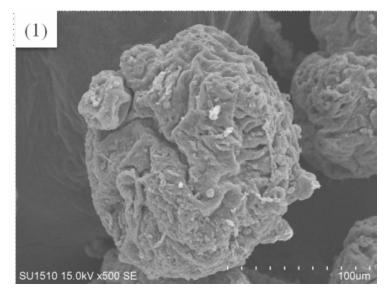
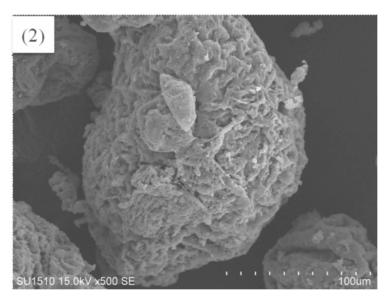
Figure 1 shows the SEM images of PVC resin products obtained by using different hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
(1)—Imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
(2)—Domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
Fig. 1 SEM of resins produced in 10-L polymerizer in the presence of different hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the surface structures of the PVC resin particles produced by different cellulose dispersants are relatively similar.
To sum up, it can be seen that the domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose tested in this paper has the feasibility of replacing imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
3. 2 Comparative analysis of the quality of PVC resin with high polymerization degree in production test
Due to the high cost and risk of the production test, the complete replacement scheme of the small test cannot be directly applied, so the plan is to gradually increase the proportion of domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in the formula. The test results of each batch are shown in Table 3 shown.
Table 3 Test results of different production batches
|
Batch |
m (China hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose): m (imported hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose) |
Apparent density/(g/mL) |
Viscosity number/(mL/g) |
Plasticizer absorption of 100 g PVC resin/g |
Volatile matter/% |
|
0# |
0:100 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.12 |
|
1# |
1.25:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.11 |
|
2# |
1.25:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.13 |
|
3# |
1.25:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.10 |
|
4# |
2.50:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.12 |
|
5# |
2.50:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.14 |
|
6# |
2.50:1 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.18 |
|
7# |
100:0 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.11 |
|
8# |
100:0 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.17 |
|
9# |
100:0 |
0.45 |
196 |
36 |
0.14 |
It can be seen from Table 3 that the usage of domestic hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is gradually increased until the domestic hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose completely replaces the imported hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. The main indicators such as plasticizer absorption and apparent density did not fluctuate significantly, indicating that the domestic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose selected in this paper can replace the imported hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in production.
4 Conclusion
The test of domestic hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose on a 10 L small test device shows that it has the feasibility to replace imported hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose; the production substitution test results show that domestic hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used for PVC resin production, the main quality indicators of finished PVC resin and imported hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose have no significant difference. At present, the price of domestic cellulose in the market is lower than that of imported cellulose. Therefore, if domestic cellulose is used in production, the cost of production aids can be significantly reduced.
Post time: Nov-04-2022